

a positive relationship between tax rates and tax revenues.Ĭ. an inverse relationship between tax rates and tax revenues.ī. real GDP above the level it would have reached in the absence of the government's construction spree because this expenditure would have been undertaken by universities. real GDP above the level it would have reached in the absence of the government's construction spree because there is a multiplier effect. real GDP above the level it would have reached in the absence of the government's construction spree because both the government and the universities would require borrowed funds.ĭ.
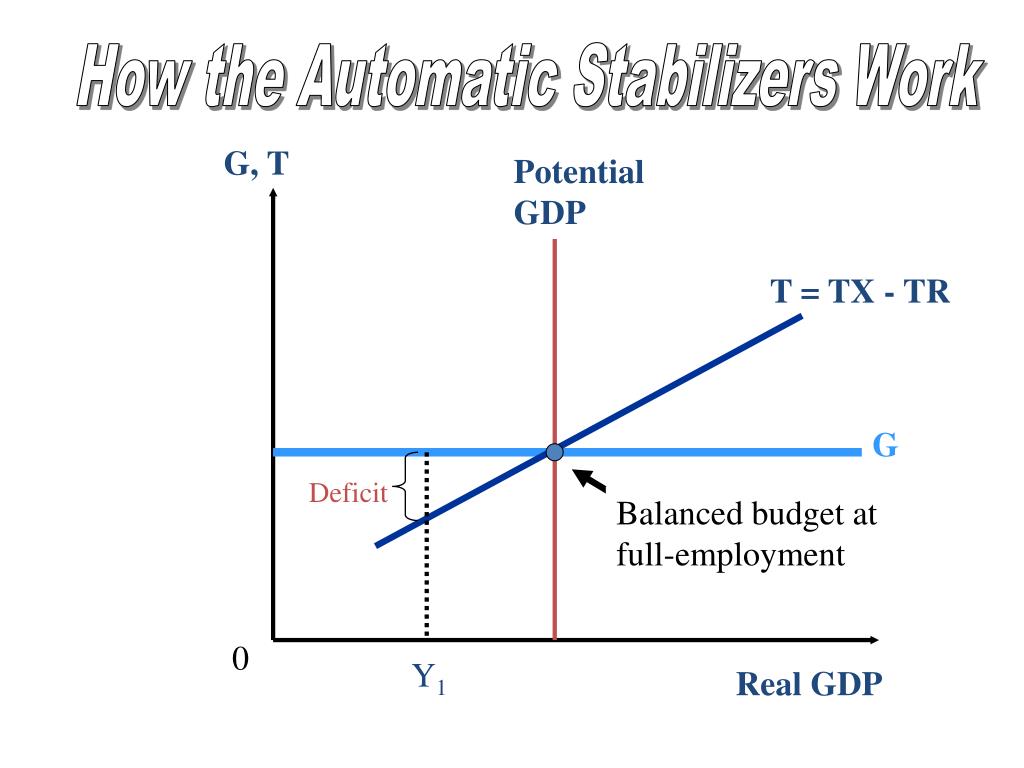
real GDP above the level it would have reached in the absence of the government's construction spree because the universities dropped their plans.Ĭ. real GDP above the level it would have reached in the absence of the government's construction spree because this expenditure would have been undertaken by universities.ī. The government's $1 billion expenditure willĪ. After construction on the government buildings began, however, the universities dropped their plans. Prior to the government's decision to construct these buildings, a few universities had been planning to build essentially the same facilities using privately obtained funds. government is in the midst of spending more than $1 billion on seven buildings containing more than 100,000 square feet of space to be used for study of infectious diseases. The Fed's contractionary monetary policy.ĭ. Which one of the following is the exception?Ī. This outcome can be explained by all of the following, except one. In fact, however, neither real GDP nor the price level changes significantly as a result of the tax cut. Suppose that Congress enacts a significant tax cut with the expectation that this action will stimulate aggregate demand and push up real GDP in the short run. Examples are the federal progressive tax system and unemployment compensation. Automatic, or built-in, stabilizers Special provisions of certain federal programs that cause changes in desired aggregate expenditures without the action of Congress and the president. Cumulative fiscal multiplier The multiplier effect of a fiscal policy action that applies to a long-run period after all influences on equilibrium real GOP have been taken into account. Impact fiscal multiplier The actual immediate multiplier effect of a fiscal policy action after taking into consideration direct fiscal offsets and other short-term crowding out of private spending. Effect time lag The time that elapses between the implementation of a policy and the results of that policy. The action time lag is quite long for fiscal policy, which requires congressional approval. Action time lag The time between recognizing an economic problem and implementing policy to solve it. supply-side economists Recognition time lag The time required to gather information about the current state of the economy.

People who support the notion that reducing tax rates does not necessarily lead to reduced tax revenues are called _ _. Supply-side economics The theory that creating incentives for individuals and firms to increase productivity will cause the aggregate supply curve to shift outward.
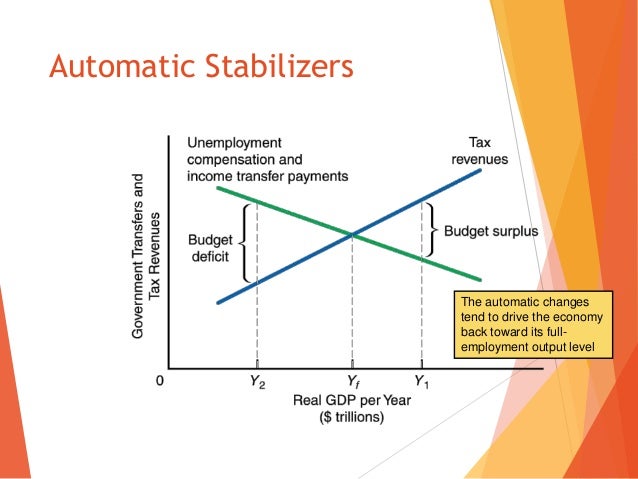
#Automatic stabilizers are defined as quizlet full
Otherwise stated, if there is a full direct expenditure offset, the government spending multiplier is zero. In the extreme case, the direct expenditure offset is dollar for dollar, so we merely end up with a relabeling of spending from private to public. Whenever government spending is a substitute for private spending, however, a rise in government spending causes a direct reduction in private spending to offset it. Any increase in government spending in an area that competes with the private sector will have some direct expenditure offset. Direct expenditure offsets Actions on the part of the private sector in spending income that offset government fiscal policy actions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
